 –
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
Overview
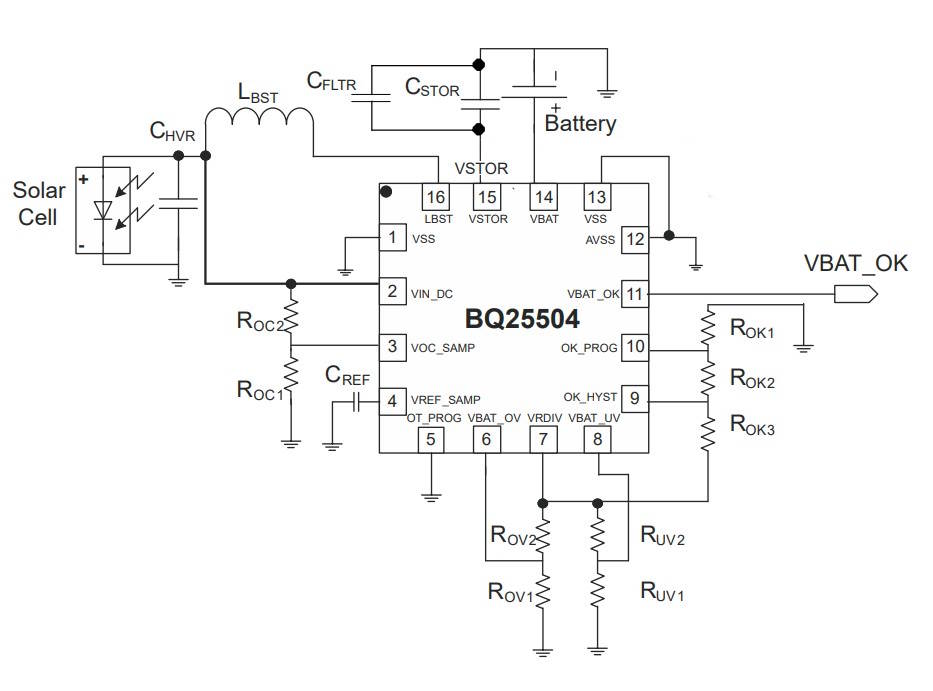
BQ25504 is specifically designed to efficiently acquire and manage the microwatts (µW) to milliwatts (mW) of power generated from a variety of DC sources like photovoltaic (solar) or thermal electric generators.
The BQ25504 is the first device of its kind to implement a highly efficient boost converter/charger targeted toward products and systems—such as wireless sensor networks (WSNs)—which have stringent power and operational demands.
The design of the BQ25504 starts with a DC-DC boost converter/charger that requires only microwatts of power to begin operating. Once started, the boost converter/charger can effectively extract power from low-voltage output harvesters such as thermoelectric generators (TEGs) or single- or dual-cell solar panels.
The boost converter can be started with VIN as low as 600 mV, and once started, can continue to harvest energy down to VIN = 130 mV.
If the calculated ideal resistor total (RSUM) isn’t available as a single 1% resistor, combine the nearest higher- and lower-value 1% parts in series, or slightly adjust RSUM up/down to match a standard value, or use two (or more) resistors in series that sum to the recommended value.
Your subscription goes a long way in backing my work. If you feel more generous, you can buy me a coffee:
